Artificial Intelligence: Is AI ready for marketing? Are marketers ready for AI?
AI (artificial intelligence) was once a “nice to know” topic for marketers. Now it’s “need to know.”
Among the big AI questions that arose in the Marketing Profs B2B (business to business) Conference (#MPB2B) were these:
- How do AI and marketing fit together?
- Is AI ready for marketing?
- Are marketers ready for AI?
- Will AI cost marketers their jobs?
Disclaimer: I’m no AI expert, just a marketer armed with curiosity and a beginner’s mind.

This blog summarizes what I learned from Chris Penn @TrustInsights, who discussed the present and future of B2B marketing analytics at MPB2B.
Is AI ready for marketing? It’s early in the game.
What is AI? It’s like teenage sex, everyone talks about it. No one does it,” Chris said.
He outlined these challenges facing analytics in marketing:
- Volume, since data created will amount to 120 zettabytes a year by 2015.
- Variety, since with 8,000 different types of marketing software, many analytics can’t be compared apples to apples.
- Velocity, since speed, is one competitive advantage AI confers.
- The veracity of analytics, since “garbage in garbage out” applies to AI.
- Value, since fewer marketers use analytics today than did earlier in 2018.
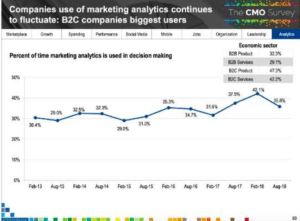
Chris tracks marketers’ use of analytics to drive decision-making. He found that:
- Marketing use of analytics doesn’t grow in a straight line; it’s up and down. The use of analytics to drive decisions declined to 35.8% in August 2018, down from 42.1% in February 2018.
- More B2C (business-to-consumer) marketers use analytics to make decisions than B2B marketers do. Almost half of B2C marketers (47.3%) use analytics, compared with one-third of B2B marketers (32.3%).
Chris outlined 5 stages in analytics usage:
- Descriptive
- Diagnostic
- Predictive
- Prescriptive
- Proactive.
What is AI? It ain’t magic. It’s math.
“All AI begins with statistics and probability,” Chris said.
- AI starts as an algorithm.
- Next AI progresses to machine learning, which he described as “We give them data, they give us software.” Machine learning can be supervised, as it was when IBM Watson solved a thorny leukemia case, or it can be unsupervised.
- Then AI advances to deep learning, which is to “tie machine learning together like layers of pancakes,” Penn says.
One example of deep learning is Google Translate, which detected patterns common to more than 100 languages and derived a proto-language. Since that happened a couple of years ago, the quality of Google translations has improved markedly.
When you use Google Translate, for example, it translates from French into its proto-language into English.
If you don’t understand how that works, don’t worry. “No one in the world, including Google, understands how the Google algorithm works,” Penn said.
What AI is good at
AI is best at working on the known knowns. It also can address the unknown knowns.
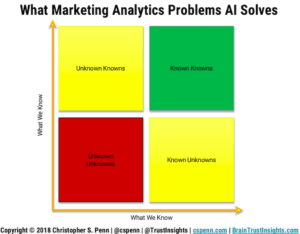
Why use AI? Because AI brings marketers these benefits:
- Acceleration, getting results faster than humans can
- Accuracy that’s better than humans can achieve
- Automation of routine work and processes.
AI finds patterns in historical data to deduce what’s happening and what’s likely to happen next, based on historical data.
AI best answers questions that begin with who, what, and when?

- AI solves who? questions with network diagrams and improved lead scoring.
- AI solves what? questions such as reverse-engineering Google and attribution analysis.
- AI solves when? questions with predictive analytics.
Who?
AI is good at finding connections among people. For example, AI can rapidly create a network diagram of your Twitter connections.
What?
A year ago, I was trying to extract meaning from 1,500 questions marketers had asked in my content marketing workshops. But extracting that meaning wasn’t possible with brainpower and persistence alone.
I’d made a big spreadsheet of questions, found a few patterns, realized they revealed very little, then got stuck. I couldn’t mine the insights I’d hoped for from 1500 questions.
Taking Chris’ advice, I found a data analyst who used Python and R to identify the 100 most important questions from among the original 1500 questions.
That use of AI-enabled me to start writing a series of blogs on the Top 100 Questions on content marketing. So far, I’ve answered 59 of these Top 100 Questions.
Processing that huge set of questions to extract meaning is how I found out first-hand that AI works.
AI solved my problem, got the job done, and delivered even more than I’d expected. For example, it enabled me to:
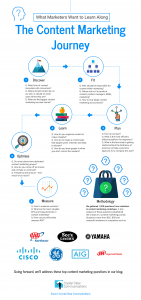
- Map the 6-step journey that marketers go through to adopt content marketing. Here’s an infographic of the content marketing journey.
This infographic maps marketers’ questions to the 6 steps in the content marketing journey. - Find the biggest stumbling block for consumer marketers who use content marketing – attribution, one kind of problem that AI can help marketers solve.
- Find the biggest stumbling block for B2B marketers – organizational fit, the kind of problem it takes humans to solve.
When?
AI can solve time-series forecasting problems, such as the seasonality of products.
For example, Chris shared a chart to show which kinds of cheese are likeliest to sell during each week in a year. That’s fantastic to know if you’re a cheese producer.
Another example: Chris applied AI to predict the best and worst weeks to send your quarterly mega-content emails in 2019. That’s fantastic for marketers to know as they plan editorial calendars for content marketing.
If you plan to send big quarterly emails in 2019, for maximum results, send them:
- Q1 2019: the week of January 19
- Q2 2019: the week of April 21
- Q3 2019: the week of September 15
- Q4 2019: the week of October 21.
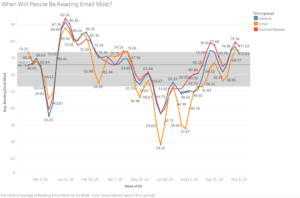
The worst weeks to send your mega-content quarterly emails are:
- Q1 2019: the week of March 10
- Q2 2019: the week of June 23
- Q3 2019: the week of July 28
- Q4 2019: the week of December 23.
This forecast is based on Chris’ analysis of web searches for “Outlook out of office.”
What kind of data does AI need?
The data you input to AI really matters. To get the right insights, make sure your data are:
- Clean
- Complete
- Compatible
- Chosen well
- Comprehensive.
7 Steps in Companies’ AI Journey
Chris laid out the 7 steps in the company’s journey to get the most from AI:
- Data Foundation: find, clean, prepare, and unify data
- Measurement & Analytics: identify and measure KPIs, and understand what happened
- Insights & Research: qualitative capabilities, explain the data story, market research
- Process Automation: automate the known knowns, find efficiencies, scale up processes
- Data science: explore the unknowns, build statistical and math capabilities, code and engineering
- Machine learning: Advanced process automation and data science with supervised or unsupervised learning, reinforcement learning
- AI-powered: adopt AI across the organization in every role.
What AI can’t do
AI can’t answer the question why?
AI can’t replicate human activities. Don’t look to AI for empathy, judgment, general life experience, or relationships, Chris said.
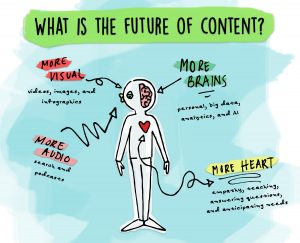
I found comfort in this advice. Why?
Because earlier this year, I predicted that the future of content marketing will need more brains, including artificial ones – and more heart, which only humans have to give.
How to get started with AI
Pick one metric to measure and analyze the **** out of it,” Chris advised.
- Hire or rent a data analyst who knows AI and works in languages such as Python or R.
- Use free tools offered by Microsoft, Amazon, Google, and IBM Watson.
- Learn R and Python if you want to go deep.
- Build a team that includes developers to extract data; data scientists to structure, architect, and process data; and marketing technologists to apply AI.
“It takes multidisciplinary skills and algorithmic thinking” to succeed, Chris said.
In the future, there will be 2 kinds of jobs. Either you will manage the machines, or the machines will manage you.”
You can access a video of Chris Penn’s presentation at the Marketing Profs B2B Conference here.

“Is AI ready for marketing? Are marketers ready for AI?” are not among marketers’ Top 100 Questions on content marketing — yet. Here are answers to the Top 100 Questions on content marketing.